The benefits of globalization have diminished in recent years due to tensions in the US-China relationship. In 2020, fear of COVID spread, which further disrupted production and supply chains and deepened market instability. This situation recalls the 30 year-old movie Sister Act, in which a lounge singer played by Whoopi Goldberg disguised herself as a nun to escape her gang, and accidentally ended up as a choir director, turning the troubled and uncoordinated choir into a refreshing rock-gospel group. Street youth were attracted to the church, which not only repaired the relationship between the church and the nearby residents, but also brought positive changes to the community. This story eventually moved even the Pope.
In this turbulent situation, governments lack coordination and mutual trust. We need to think pro-actively about how to create industrial differentiation, growth influence and solid international relations. We still hope to transform the rock gospel “I will follow him” into the trends you and I should follow in the next 10 years, 100 years after the 1911 Revolution: the dynamic revolution, digital infrastructure and DNA reprogramming.
Delivery is the foundation of the space market
In mid-October, Chairman of the US Joint Chiefs of Staff General Mark Milley confirmed an exclusive report by the Financial Times that China’s People’s Liberation Army twice test-fired advanced hypersonic missiles in July of this year, surpassing the imagination of US intelligence. Reports have emphasized that US military scientific research units could not believe that “Chinese weapons could break through the limitations of physics.” These weapons may also trigger a new Sputnik crisis in the century following the US-Soviet Cold War.
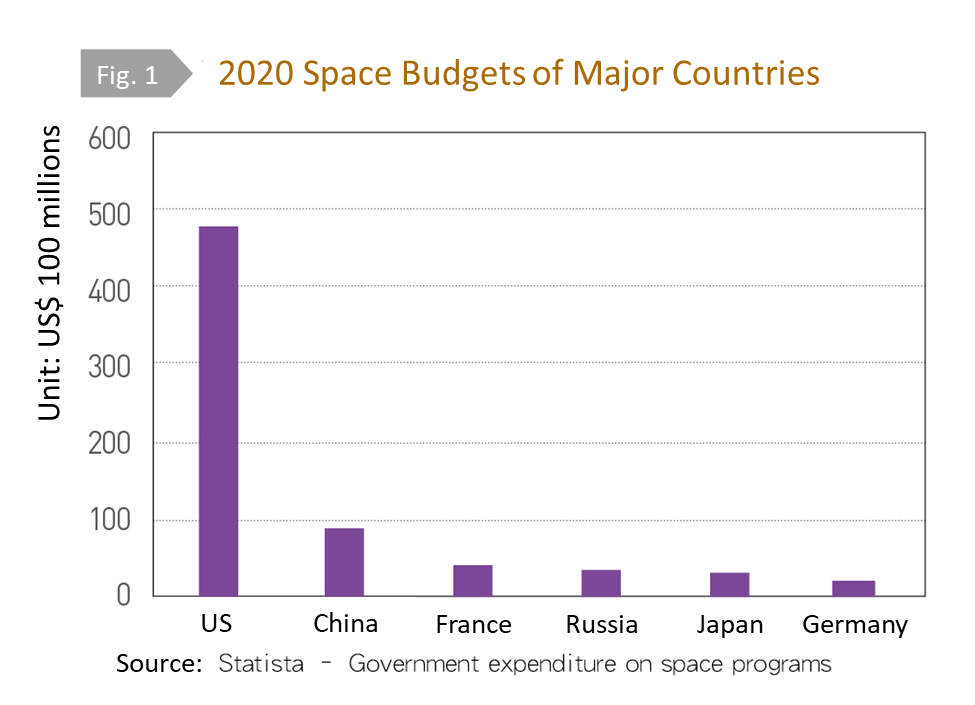
Although the general public does not see the risk of war and conflict, especially when it involves a threat from space, the government and the private sector must also prepare investments in appropriate deterrence capabilities. If we want to occupy a place in the future low-orbit satellite market to facilitate next-generation of wireless big data, homeland security monitoring, and climate/environmental observation, the need for space delivery research and development and innovation is obvious. The US and China have invested tens of billions of dollars in their space budgets, but other international powers have an investment gap (Fig. 1). We must think about cooperation with limited resources and a complex international situation in order to reach space. The author proposes two measures to achieve the political space and economic scale necessary to enter space.

1. Civilian-military cooperation. In 1987, the Industrial Technology Research Institute and the Dutch company Philips jointly established TSMC. Today, Taiwan’s Academia Sinica also has mature missile thruster technology, while the private sector has the electronic chips, aviation parts and other experience required for European and American spacecraft. If, e.g. a space power concept joint venture company could be established with an appropriate partner, it could also bring the next wave of industrial business opportunities following the semiconductor revolution of the 1990s. Although the process of building something from scratch involves great initial cost pressure and risks, Taiwan's self-developed space economy could match its current international status in semiconductors.
2. Strategic cooperation with international partners. Whether it is the private space delivery companies currently operating in the US, start-ups which have conducted flight tests for small and medium-sized low-orbit rockets, or even government units with relatively limited budgets in Europe and Japan, we can earn good returns from appropriate capital financing in technology. This could include partial localization of delivery technology and priority use of launches. This method could reduce the initial risk through proven international experience, but will also inevitably sacrifice a certain degree of independent control and research opportunities.
Digital infrastructure, the global backbone of information technology
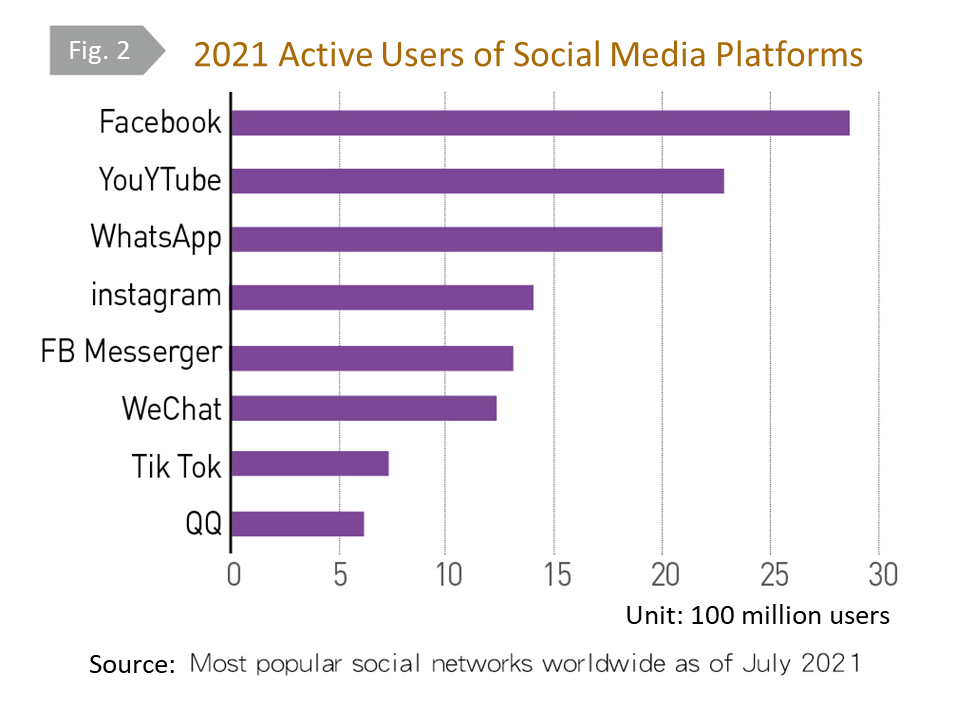
Also in October, in addition to China’s breakthrough in space weapons, Facebook, Instagram, and WhatsApp crashed for 6 hours. A whistleblower mentioned concerns about the Facebook algorithm related to user manipulation and profitability. In addition, we can also see that social platforms are shifting to the meta-universe concept to create new business opportunities. These digital platforms reach billions of people around the world (Fig. 2), affecting our discourse, communication methods, and business models. Therefore, we must also consider how to grasp opportunities and manage the corresponding information security and misinformation risks in the digital world.
For example, US President Joe Biden’s next US$ 1 trillion infrastructure plan also includes construction of network broadband. As a high-tech manufacturing center, in addition to the aforementioned low-orbit communication satellites, the Taiwanese government and businesses should also think about establishing strategic cooperation in digital infrastructure.
Everything comes from genetics
From the dream of resurrecting dinosaurs in the ‘90s movie Jurassic Park, to recent veggie burgers made through DNA modification, and the mRNA technology against the coronavirus last year, synthetic biology has seen explosive growth and development potential in recent years. According a 2019 report by the World Bank, the cost of gene sequencing has dropped from nearly US$3 billion 15 years ago to US$ 1,000, and is expected to fall by another factor of ten in the next five years. Humans will be able to read and write any DNA as code, and to quickly replicate and produce the biological characteristics of yeast and bacteria.
According to a report entitled Synthetic Biology Global Market Report 2021: COVID-19 Growth and Change to 2030, synthetic biology has grown from a market value of US$ 8.64 billion in 2020 to US$ 10.07 billion this year. The report forecasts that the market will reach US$ 28.91 billion in 2025. Using the mechanisms of nature to reverse engineer DNA, it seems that mankind is moving closer to solving food supply, biochemical energy, medical and health issues, and global warming. Cooperation with startups and training of bio-hacking talent will be topics of utmost importance over the next decade.
Musicians do not retire until there is no music in their hearts
Even if rockets existed in the 1960s, digital network communications in the 1990s, and synthetic biology since 2000, we still need to pay attention to its investment links and long-term strategic impact on national industries. It is only once certain resources are in place that leaders with vision, like Deloris in Sister Act, can implement their visions of transformation.
The author of this article is currently working at a foreign bank in Taiwan, and has served as an executive at several foreign banks and financial information companies in the Asia Pacific.